This post is highlight the speed benefit of CRAM files over BAM files as it seems to not be widely used.
CRAM files are often about 50% of the size of an identical BAM for lossless compression largely due to not saving the sequence of each read, instead keeping only the delta to the reference sequence for the alignment. Additional savings can be gained from lossy compression of base-qualities and read-names.
The htslib implementation of CRAM has an additional advantage beyond file size: speed. It allows the user to specify
which of the pieces of the alignment will be needed and it only decodes those. (While this is possible in BAM format, for example as
implemented in pybam it is not available for BAM via htslib.) This control can
greatly speed processing when only a few pieces of the alignment are needed. This is quite useful since CRAM parsing can otherwise be
the bottleneck for much genomics work.
In short, the most costly fields to decode are:
- base-qualities
- sequence
- aux tags
It’s possible to get better speed and parallelization by not decoding combinations of these. The plot below shows time on the Y-axis (lower is better) that it took to iterate through chromosome 20 of my test cram for exclude::thread combinations on the X-axis.
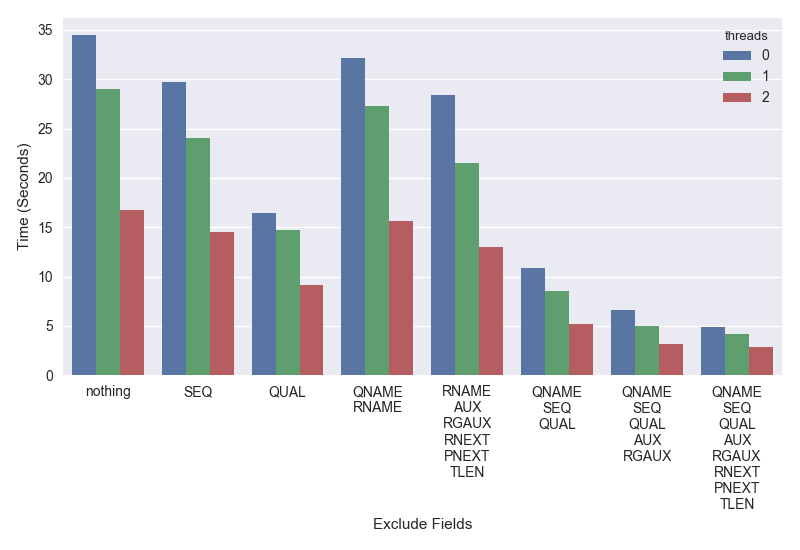
The bars a grouped by the excluded fields and colored by the number of decompression threads used.
Interested readers can study this in more detail, but the key points are:
- It’s possible to get a 2X speed improvement simply by not parsing the base qualities (QUAL).
- If you don’t need SEQ, QUAL (base-qualities), AUX (tags like NM, SA, etc) and RG (read-groups) you can get a 3 to 4X speedup.
This is part of what makes mosdepth so fast to calculate depth on CRAM as it does not need the base-qualities, sequence or read-groups. That’s how I learned about this feature of CRAM.
We have recently used this to speed up svtyper which uses pysam; you can see how to do that here And we’ve added it to lumpy to make pre-processing alignments about twice as fast for CRAM.
These options are available from the commandline samtools via --input-format-options required_fields=#### which is documented here
I have gisted the nim code to do these timings the the python script for plotting here in case anyone wants to try various combinations.